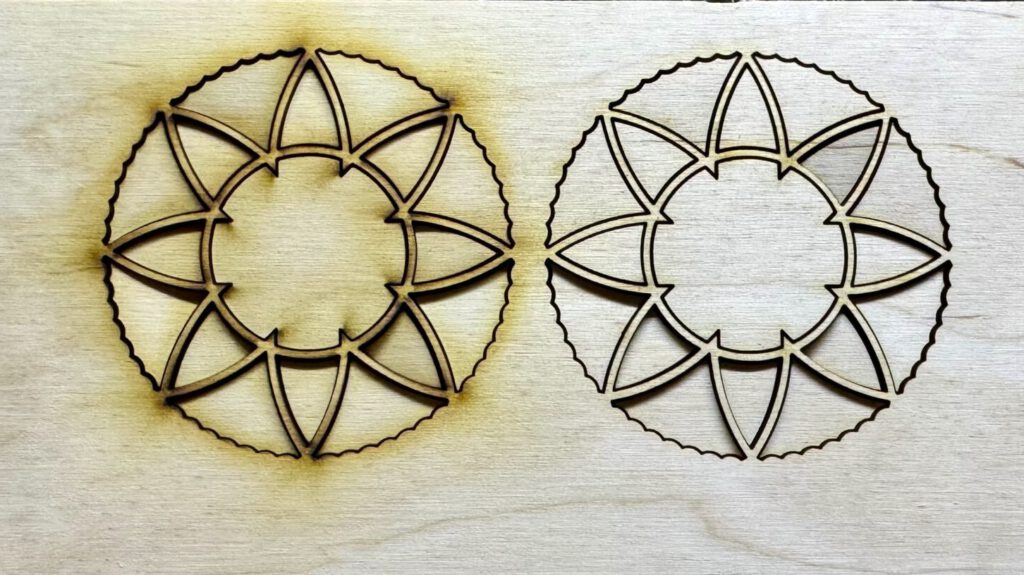
If you’re using a CO2 laser for engraving or cutting projects, choosing the right CO2 laser lens is crucial. The lens focuses the laser beam and directly impacts how efficiently and cleanly your laser operates. To increase the lens’s lifespan, it’s coated using one of two common methods: CVD vs. PVD. Both have their pros and cons, but in most cases, CVD is the better choice for hobby laser users. The lens material also plays an essential role. In this guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know to choose the right lens.
What Materials Are CO2 Laser Lenses Made Of?
CO2 laser lenses are typically made from two main materials: ZnSe (Zinc Selenide) and GaAs (Gallium Arsenide). Each has specific properties that make it suitable for different applications.
ZnSe Lenses
Zinc selenide is the most commonly used material for CO2 laser lenses. It features high transparency in the infrared range (10.6 µm) and excellent thermal stability.
Advantages:
- High light transmission: Perfect for precision applications.
- Versatile: Suitable for hobby lasers and professional applications up to ~100 watts.
- Affordable and widely available.
GaAs Lenses
Gallium arsenide is primarily used in high-power CO2 lasers exceeding 100 watts. This material is extremely durable and better resists high temperatures and intense laser beams than ZnSe.
Advantages:
- Extremely heat-resistant: Ideal for continuous operation.
- Durable, especially for demanding power requirements.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than ZnSe.
Lenses with CVD vs. PVD Coating
Besides the material, the lens coating is also crucial. Coatings protect the lens from dirt and scratches while improving heat resistance.
CVD Coating
The CVD process (Chemical Vapor Deposition) uses chemical vapor deposition to create a solid, thick protective layer on the lens. This coating is robust and resistant to dust, heat, and wear.
Advantages:
- Lower maintenance due to better resistance to dirt.
- Highly durable and long-lasting.
- Perfect for hobby applications with medium to high demands.
PVD Coating
PVD coating (Physical Vapor Deposition) is thinner and applied through physical methods. It enables precise light direction but is less robust.
Advantages:
- More affordable than CVD.
Disadvantages:
- Less durable: Not ideal for dusty environments or prolonged use.
- Shorter lifespan, especially under intensive use.
PVD is used for specialized applications where optical precision matters more than durability. However, due to its lower robustness, I don’t recommend it for workshop or hobby use.
Which Lens Is the Best Choice for You?
For most hobby applications, a CVD-coated ZnSe lens* is the ideal choice. It’s versatile, durable, and delivers reliable results even under heavy use. Its high transparency and heat resistance make it suitable for cutting and engraving. This is my clear recommendation.
The more affordable alternative is a PVD-coated ZnSe lens*. However, given the relatively low cost of a lens, I recommend investing in the longer-lasting CVD lens.
For CO2 lasers with over 100 watts of power, you’ll need a GaAs lens* with a CVD coating. While more expensive, it offers the robustness and heat resistance needed for reliable performance under intense use.
ADVERTISEMENT: The links marked with an asterisk (*) are affiliate links. If you click on such a link and make a purchase on the destination page, we receive a referral commission from the respective provider or online store. This helps us cover our costs (e.g., web hosting). There are no additional costs or price disadvantages for you when purchasing.